Preparing students for life beyond their schooling involves so much more than academic achievement. Students today not only need to excel in their traditional studies, but also develop skills and understanding of technology, media literacy, and critical thinking (just to name a few). Globalization and technological advancement make these components vital for competency in the 21st century workforce. To assist students in developing the competencies required to be successful beyond the classroom, educators weave these skills into learning experiences through STEAM, Project-based Learning, blended learning, student-led learning etc.
In this article, we’ll explore the most important 21st century competencies that educators should be helping students develop through STEAM Project-based Learning.
What are the 21st century competencies students need to move into the future?

In addition to basic subject-area knowledge, there are a combination of competencies students must develop in order to be set up for long term success in the 21st century workforce. These competencies fall under 3 different categories that make up the 21st century framework: Core Values, Social Emotional Skills, and 21st Century “Success” Skills.
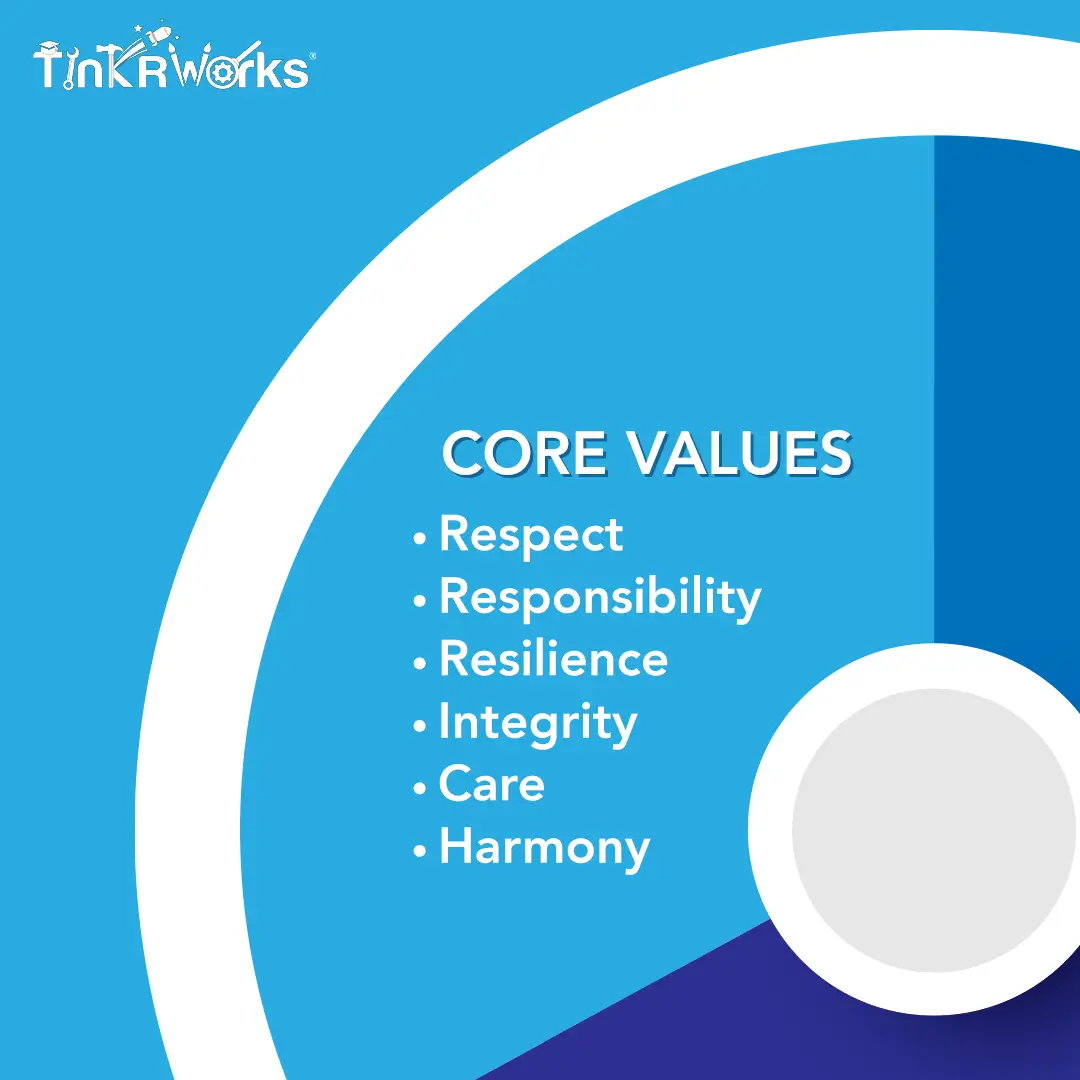
Core Values
Core values create a framework with which students can shape their beliefs, attitudes, and actions. While cultural values vary and are passed on from generation to generation, some values are universal and are embedded in classroom practices around the world. . To help you formulate your list of core values, check out these examples from the Ministry of Education Singapore:
- Respect: Students should understand how respecting themselves, others, and even the resources available to them makes the world a better place.
- Responsibility: Taking responsibility for their actions, belongings, and output makes students more self-sufficient and motivated in the long run.
- Resilience: In the face of challenge and adversity, resilience helps students persevere, which ultimately helps them learn and grow to their greatest potential.
- Integrity: When students begin to understand that their integrity creates the view that their fellow students and teachers have of them, they become determined to conduct themselves with honesty and honor.
- Care: Whether caring for their feelings, the feelings of their peers, or the feelings of their teachers, students learn how their own actions and attitude can influence those around them.
- Harmony: All of these values working together in synchrony creates a harmony of focused, driven, and positive environments in any classroom.
Social-Emotional Skills
The competences that characterize Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) and STEM/STEAM are key ingredients of success in the 21st century. SEL and STEM overlap in meaningful ways and have a profound impact on behavior, development, academic achievement, and professional success. They provide the foundational skills students need to be future-ready professional and community members. Here are some main areas of overlap between SEL and STEAM.
- Self-awareness: The ability to accurately recognize one’s own emotions, thoughts, and values and how they influence behavior.
- Self-management: The ability to successfully regulate one’s emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in different situations — effectively managing stress, controlling impulses, and motivating oneself.
- Social awareness: The ability to take the perspective of and empathize with others, including those from diverse backgrounds and cultures.
- Responsible decision-making: The ability to make constructive choices about personal behavior and social interactions based on ethical standards, safety concerns, and social norms.
- Relationship skills: The ability to establish and maintain healthy and rewarding relationships with diverse individuals and groups.

21st Century “Success” Skills
21st century “success” skills prepare students for college, work, and citizenship. STEAM education is an effective way to help students strengthen these 21st century competencies:
- Critical- and analytical-thinking: When students are able to look beyond a surface level at information and media presented to them, they become more self-reliant in their approach to understanding the world around them.
- Problem Solving: Teaching students to approach problems with eagerness and understanding sets them up to solve problems across a variety of subject areas and difficulty levels. Even in their personal lives, students will benefit from the problem-solving practice they receive in their classrooms early on in their education.
- Receiving and utilizing critical feedback: Learning how to productively listen to and act on feedback from peers, educators, or coaches makes students more resilient while showing them new ways to approach problems or challenges.
- Learning from mistakes: Productive failure is vital for any person in any field. Though this skill can be best-developed through STEAM projects, it is important to problems across all fields of study.
- Weighing sources for importance and credibility: As an extension of critical thinking, the ability to assess the credibility of a variety of sources can help students outside of the classroom or workforce. This skill helps students in their daily personal lives as they grow into adults who make decisions and contributions in their communities.
- Drawing inferences and reaching conclusions independently: While group-based work and projects help students build several fundamental skills like teamwork and compromise, students need practice reaching conclusions on their own. Though it can be difficult, especially for younger students, this helps them build confidence in their own abilities and instincts.
- Time management: The ability to properly manage tasks and deadlines to ensure that assignments and projects are completed on time makes students successful in the classroom and the working world beyond.
- Innovation and creativity: When facing any problem or challenge, innovation and creativity give students an edge. These skills help them find new ways to solve existing problems, which makes them productive team members.
- Teamwork: No one succeeds alone, which means that team-based skills like communication, cooperation, and collaboration are necessary to all members of the workforce

In Summary
Equipping students with the skills they need for life beyond their schooling is more complex today due to globalization and technological advancements. Educators have the power to foster core values, Social Emotional Skills, and 21st century competencies in students through STEM/STEAM learning. When these elements work cohesively in the minds of students, they create self-sufficient and driven contributors to the 21st century workforce.
Interested in strengthening your students’ 21st century “success” skills? Get started with STEM Project-based Learning with our educator-curated Makerspace Lesson Library – TinkRpedia. This STEAM library features free, hands-on projects that cover a variety of subjects and difficulty levels. Try it today and see why educators love it!


